【Arduino&Pmod NAV】地磁気センサからヨー軸算出
前書き
加速度センサとジャイロセンサを使って姿勢角を算出するのは、以前に複数個の記事で行っています。
shizenkarasuzon.hatenablog.com
shizenkarasuzon.hatenablog.com
ですが、今回は地磁気センサを使って姿勢角(ヨー角のみ)を算出してみようと思います
部品
僕の環境では以下の部品を使いました。
これを、以下のように接続します。
Arduino UNO の場合:
PmodNAV<---> Arduino pin 6 3.3V pin 5 GND pin 4 A5 pin 2 A4
Arduino Due の場合
PmodNAV<---> Arduino pin 6 3.3V pin 5 GND pin 4 21(SCLピン) pin 2 20(SDAピン)
繋げるとこんな感じになります。

3軸地磁気センサについて
地磁気センサ(電子コンパス)は地球の磁力を検出するセンサで、「北」の方角にあたるような方向を三次元(2次元のものもある)のベクトルで計測します。理想的な状態を考えると、センサを回転させると計測値 は原点を中心とする球の表面上に分布するはずです。(二次元の場合は円周上)
しかし、実際には周辺地場の影響により、ベクトルが少し平行移動してしまいます。そこで、それを補正する必要があります。具体的には、測定した値は中心が原点からずれた球の表面上に分布するような感じになります。そこで、三軸地磁気センサの場合は球補正、二軸地磁気センサの場合は円補正をする必要があります(下の節で円補正しています)
そして、補正した値を使えば、ヨー角 を算出することができます。
センサーが水平に設置されている場合の算出は簡単で、です。
しかし、センサーが傾いていると、以下の式の様になるようです。
参考→3軸方位センサを用いた姿勢推定 – Watako-Lab.
ここで、は地磁気センサの測定値、
はpitch角のcos,
はroll角のsinを表しています。
pitchとrollは地磁気センサから求められないので、加速度センサなどから求める必要があります。
動作確認(センサ値取得)
とりあえず、PmodNAVで地磁気センサの値を測定してみます。
// Arduinoプログラム。地磁気センサの計測値(m_x, m_y, m_z)をシリアル通信でPCの送る) #define RAD_2_PI 57.3248 #include <Wire.h> #include <SparkFunLSM9DS1.h> float magX, magY, magZ; double pitch, roll, yaw = 0; #define LSM9DS1_M 0x1E #define LSM9DS1_AG 0x6B LSM9DS1 imu; void setup(void){ Serial.begin(115200); // initialization of serial communication imu.settings.device.commInterface = IMU_MODE_I2C; // initialization of the module imu.settings.device.mAddress = LSM9DS1_M; imu.settings.device.agAddress = LSM9DS1_AG; if (!imu.begin()){ Serial.println("Probleme de communication avec le LSM9DS1."); while (1); } accX = imu.ax; accY = imu.ay; accZ = imu.az; gyroX = imu.gx; gyroY = imu.gy; gyroZ = imu.gz; delay(100);//Wait for sensor to stablize } void printAttitude(void){ Serial.print(imu.mx); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(imu.my); Serial.print(","); Serial.println(imu.mz); delay(2); } void loop(){ if (imu.magAvailable()) imu.readMag(); magX = imu.mx; magY = imu.my; magZ = imu.mz; printAttitude(); }
↑のプログラムをArduinoに書き込み、Processingでリアルタイムでプロットしてみます。
//Processingのプログラム。USBでArduinoとつないでから実行してください float x,y,z; import processing.serial.*; Serial myPort; float pitch, roll, yaw; String myString; PImage img; int window_size = 800; void setup() { myPort = new Serial(this, "COM4", 115200); //COMポートの番号は環境によって設定してください。デバイスマネージャー等で確認できます。 myString = ""; frameRate(30); smooth(); myPort.bufferUntil('\n'); pitch = 0; roll = 0; yaw = 0; background(0,0,0); size(800, 800); stroke(255, 0, 0); line(0, window_size/2, window_size, window_size/2); stroke(0, 255, 0); line(window_size/2, 0, window_size/2, window_size); noFill(); stroke(255,255,0); rect(window_size/2 - 100, window_size/2 - 100, 200, 200); } void draw() { int sensors[] = int(split(myString, ',')); if (sensors.length > 2) { x = sensors[0] / 10 + window_size/2; y = sensors[1] / 10 + window_size/2; noStroke(); fill(0,255,255); ellipse(x,y,5,5); println(myString); } } void serialEvent(Serial myPort){ myString = myPort.readStringUntil('\n'); if (myString != null) { myString = trim(myString); } }
すると、こんな感じになります
今回の目的はセンサーを水平に固定した状態でヨー角を測定することなので、と
をプロットしています。ほんとはきちんと水平を測って測定しないといけないんだろうけど、適当にやったので測定値が分散してしまっています。

赤と青の直線の交点が原点ですが、センサーの測定値の円(?)の中心が原点から大きくずれていることは確かでしょう。ということで、円補正に入ります。
円補正
先ほどプロットしたの値をもとに、Pythonを用いて円推定を行います。
import numpy as np import math import random import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def CircleFitting(x,y): # https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bDYDZJvVHPYのコピペです。 sumx = sum(x) sumy = sum(y) sumx2 = sum([ix ** 2 for ix in x]) sumy2 = sum([iy ** 2 for iy in y]) sumxy = sum([ix * iy for (ix,iy) in zip(x,y)]) F = np.array([[sumx2,sumxy,sumx], [sumxy,sumy2,sumy], [sumx,sumy,len(x)]]) G = np.array([[-sum([ix ** 3 + ix*iy **2 for (ix,iy) in zip(x,y)])], [-sum([ix ** 2 *iy + iy **3 for (ix,iy) in zip(x,y)])], [-sum([ix ** 2 + iy **2 for (ix,iy) in zip(x,y)])]]) T=np.linalg.inv(F).dot(G) cxe=float(T[0]/-2) cye=float(T[1]/-2) re=math.sqrt(cxe**2+cye**2-T[2]) #print (cxe,cye,re) return (cxe,cye,re) #(推定した円の中心x座標, 中心y座標、半径) def main(): x_list = [] y_list = [] z_list = [] # データ読み込み with open("test.txt") as f: # シリアル通信で受信した、地磁気センサの計測値をテキスト形式で保存してあるのでそれを読み込む s = f.read().split("\n") lines = 0 for data in s: data2 = data.split(",") lines += 1 try: x_list.append(int(data2[0])) y_list.append(int(data2[1])) z_list.append(int(data2[2])) except: print("error -> line = " + str(lines) + ", data = " + str(data2)) # 円推定 (cxe,cye,re)=CircleFitting(x_list, y_list) print(cxe,cye,re) #描画 theta=np.arange(0,2*math.pi,0.1) xe=[] ye=[] for itheta in theta: xe.append(re*math.cos(itheta)+cxe) ye.append(re*math.sin(itheta)+cye) xe.append(xe[0]) ye.append(ye[0]) plt.plot(x_list,y_list,"ob",label="raw data") plt.plot(xe,ye,"-r",label="estimated") plt.plot(cxe,cye,"xb",label="center") plt.axis("equal") plt.grid(True) plt.legend() plt.show() main()
その結果、以下の画像になりました。
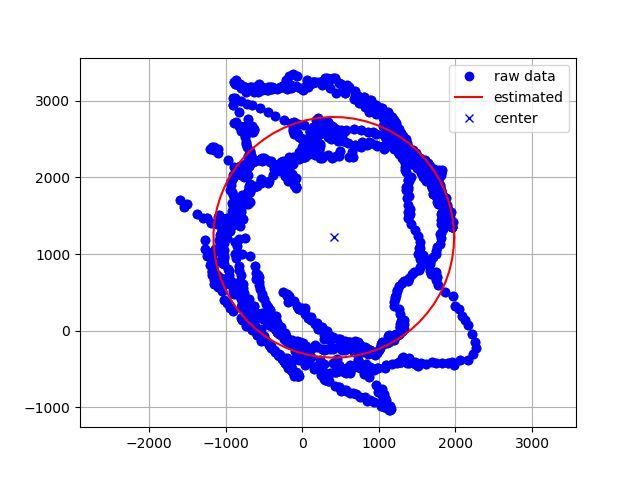
青いドットが測定した値 で、その測定値に円フィッティングを行った結果が赤い円です。
この赤い円は中心座標は(411, 1218) 半径は1570でした。つまり、周辺地場が(411, 1218) だけ働いているので、その分だけ計測値から引いてヨー角を算出する必要があります。
で、下の様なプログラムになります。
最終スケッチ
#define RAD_2_PI 57.3248 #include <Wire.h> #include <SparkFunLSM9DS1.h> double accX, accY, accZ; double gyroX, gyroY, gyroZ; float magX, magY, magZ; double pitch, roll, yaw = 0; #define LSM9DS1_M 0x1E #define LSM9DS1_AG 0x6B LSM9DS1 imu; // Creation of the object imu void setup(void){ Serial.begin(115200); // initialization of serial communication imu.settings.device.commInterface = IMU_MODE_I2C; // initialization of the module imu.settings.device.mAddress = LSM9DS1_M; imu.settings.device.agAddress = LSM9DS1_AG; if (!imu.begin()){ Serial.println("Probleme de communication avec le LSM9DS1."); while (1); } accX = imu.ax; accY = imu.ay; accZ = imu.az; gyroX = imu.gx; gyroY = imu.gy; gyroZ = imu.gz; delay(100);//Wait for sensor to stablize } void printAttitude(void){ Serial.print(pitch); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(roll); Serial.print(","); Serial.println(yaw); delay(2); } void loop(){ if (imu.gyroAvailable())imu.readGyro(); if (imu.accelAvailable())imu.readAccel(); if (imu.magAvailable()) imu.readMag(); accX = imu.ax; accY = imu.ay; accZ = imu.az; gyroX = imu.gx; gyroY = imu.gy; gyroZ = imu.gz; magX = imu.mx - 411; //値補正! magY = imu.my - 1218; // 値補正! magZ = imu.mz; /*角度を求める*/ roll = atan2(accY, accZ); pitch = atan(-accX / sqrt(accY * accY + accZ * accZ)); yaw = atan2(magY, magX); printAttitude(); }
上のプログラムを実行すると、pitch, roll, yawの値がシリアルモニタに出力されると思います。
試しにProcessingで同期してみました。うまくいっているようです。(回転方向が逆ですが)
